The content below is a segment of a longer living document produced by CDAIT: Overview of Internet of Things (IoT) Research Activity at Georgia Tech.
Overview
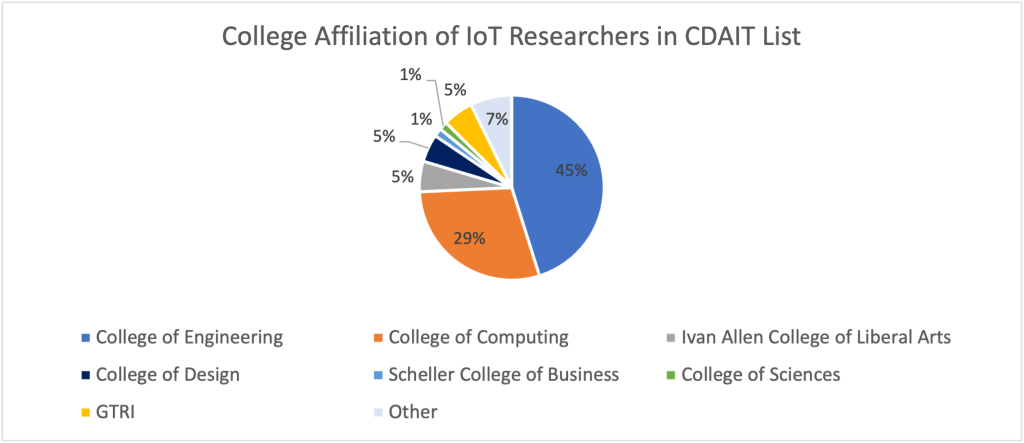
As part of CDAIT's preliminary assessment of Internet of Things (IoT) related research conducted at Georgia Tech, we have identified GT researchers currently active in IoT or IoT related technologies, software or applications. Campus wide, we have assembled a list of more than 200 researchers housed in all 6 colleges, as well as GTRI and other interdisciplinary research units or entities that are part of Georgia Tech. While all colleges at Georgia Tech are represented, most researchers conducting or interested in IoT work are within the College of Engineering and the College of Computing.
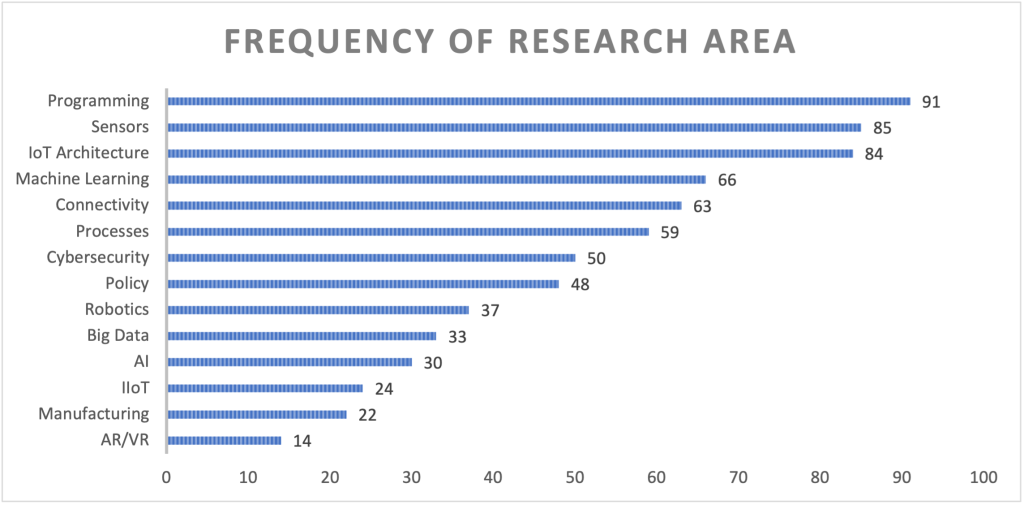
Georgia Tech researchers are, not surprisingly, well represented in the fields of IoT, and IoT-adjunct research. Cataloguing campus-wide research, we have categorized more than 700 research terms, from the activities of some 206 researchers, into 14 broad thematic areas: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Industrial IoT (IIoT), Robotics, IoT Architecture, Big Data, Connectivity, Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality (AR/VR), Manufacturing, Policy, Cybersecurity, Machine Learning, Processes, Programming, and Sensors. While there is certainly overlap across these themes, grouping them gives us the ability to more effectively examine researchers broad interests. Drilling down into the thematic classification, we see that the 6 most common technology-related interests are Programming, Sensors, IoT Architecture, Machine Learning, Connectivity, and Processes.
IoT Use Cases/Applications
While many of the research areas identified are quite specific (e.g. ferroelectric thin films), others are broad and have applications across multiple industries. For example, "sensors" as a research area is so broad as to seem overwhelming, however it shows how much innovation, applications and development opportunities exist for this technology. For example, sensors play an ever-expanding role in nearly all enterprise and business areas, including Industrial processes, Industry 4.0, manufacturing, and automotive; agriculture, healthcare, supply chains and logistics. Similarly, the “programming” category could include nearly any application of IoT, regardless of the sector. Different researchers, though, have different concentrations and ideally can work together by focusing on various aspects of the system or device that they are building.
The specifics of these research areas combined with grouping them into themes can help generate insight into not only the current applications of this research, but also the potential areas to grow into with these efforts and technologies.
This research is ongoing and will be updated accordingly.
